Life as a leader of 5G development
”Life as…” is a blog series where we dive into professionals’ everyday work life and get to learn more about their profession.
Read the section about working as an Agile coach or UX-designer.
In this part of ”Life as…” we meet Mats Johansson a Senior Marketing Director, of 5G solutions at Ericsson.

Mats has worked over 30 years at Ericsson in many different roles, such as development, product management and now marketing. He has worked extensively in many different areas, such as radio, core network, fixed network and IP-TV solutions.
Through his long experience, he has been involved in all generations of mobile systems. When he started his career, Sweden, Norway and Denmark were the leading countries in mobile telephony. It has been a huge journey, where we have gone from 2G's mobile use to today's society where almost everything can be managed via mobile, which has changed the world in a way that no one thought.
Mats will tell you more about Ericsson’s leading position in 5G and the development forward.
What challenges does the industry face and how can 5G affect the future?
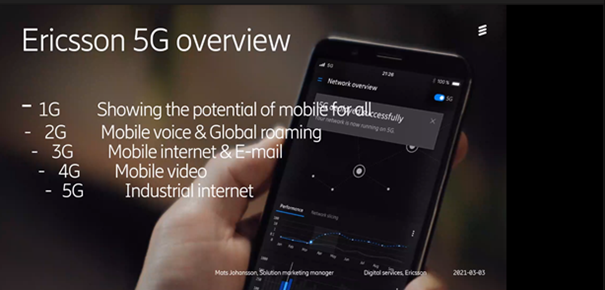
The first generation was 1G, which took off in 1980 and really showed what a mobile network could do. The breakthrough with 1G was to be able to call from mobile to mobile, but also to be able to move between different countries.
10 years has passed between each generation, in 2G mobile voice and global roaming were developed, and at the end of the 2G development, package data were added, but to a very limited extent. During this period, the internet starts to gain momentum and then 3G makes its entrance in 1991, then you have a huge belief that 3G will be a mobile internet, which it will be, but a very limited one. You could read email in your mobile phone but that was all that the internet was capable of at the time. Attempts were made with video telephony, but it didn’t work to any great extent. When 4G was introduced, the mobile internet was improved and mobile video was of higher quality.
Throughout every mobile network release, there have been people asking: What are we going to do with this? I do not need this? Even now in the development of 5G and onwards there is a certain scepticism, but it decreases with each new generation.
"5G will connect industries and use the mobile network industrially."
Up until now, the mobile network has primarily been constructed for consumers but now you see the benefits of industrial use which drives 5G development.

5G has already been implemented in some countries and Ericsson has succeeded very well with 5G, about 60-70% of the 5G networks that are running today is handled by Ericsson.
How can you use the 5G network?
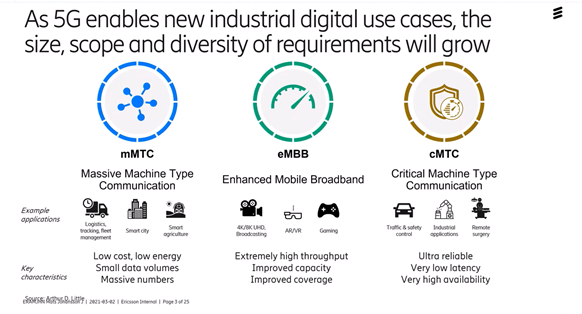
mMTC = Massive Machine Type Communication. It can be sensors, measuring points, electricity meters and being able to measure temperatures et.c. It will require reliable resources in the network but enables measurement on a large scale.
eMBB = Enhanced Mobile Broadband, i.e. an "up-heated" 4G really. Examples of services are AR, VR, gaming, where you need a short delay, for even better video quality, and user experience.
cMTC = Critical Machine Type Communication. This requires very short delays for self-driving cars and robots, where you need high reliability and high bandwidths. It remains to be seen how it will be used in full.
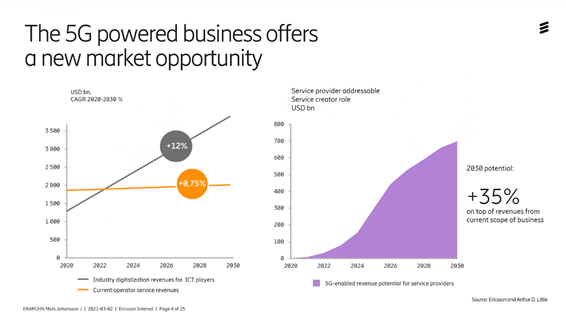
In terms of business, we see that the growth of mobile phone operators today is relatively flat. Everyone who can have a mobile phone has a mobile phone. If you look at ARPU = Average Revenue Per User, it does not increase significantly, which means that we as consumers are not prepared to spend more money per month on our monthly income for mobile use, so the development potential forward lies with companies and connected industries.
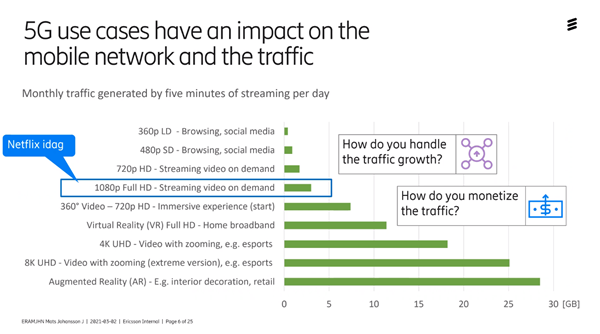
If we look at the increase in traffic going forward, it may look like in the picture below.
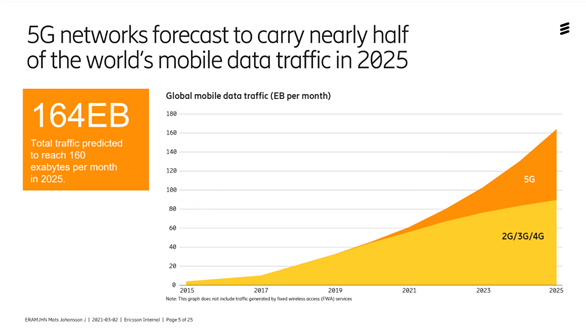
5G will increase traffic very much, so instead of measuring in megabytes and terabytes, we are up in exabytes. So 5G will lead to an increased consumption of traffic.
How will 5G affect the mobile network?
If you look at the growth potential for consumers, we see that video streaming and monthly traffic consume 2-3 GB per month if you stream Netflix for 5 minutes. Most people watch way more than that and we are simultaneously entering the VR world which will require even more data speed to get good quality.
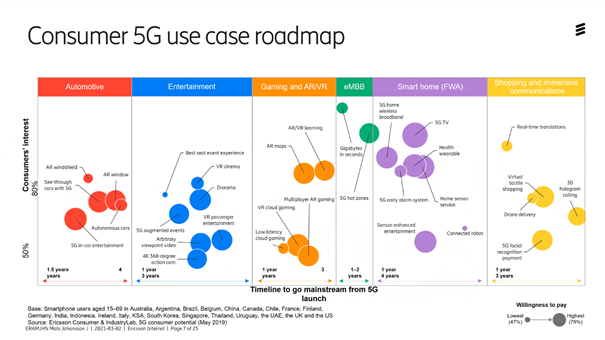
How will consumers benefit from 5G?
We see different types of services such as:
● Automotive, where you should be able to project information on the windshield, have self-driving cars and similar services.
● In Entertainment, games, VR and AR where increased network capacity will be delivered through 5G.
● In Smart homes, with connected devices at home, and fixed wireless access, where you replace the fixed access network with 5G, as it is expensive to dig fiber.
● Online shopping. Many new services could be developed here, such as 3D holograms where you might be able to feel and squeeze on products you are interested in.
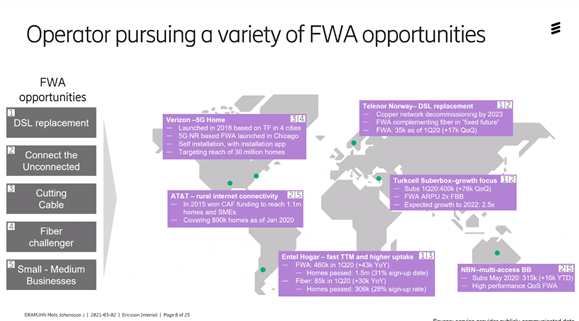
In 2019, Verizon was the first to launch 5G in a pre-standard. Their mission was to get fixed broadband to another household, ie Fixed Wireless Access. In the US, only 16% have fiber, many are not connected at all, so there is a great potential there to get better connections. It is expensive to dig fiber and then 5G can be a cost-effective option even for small and medium-sized companies.
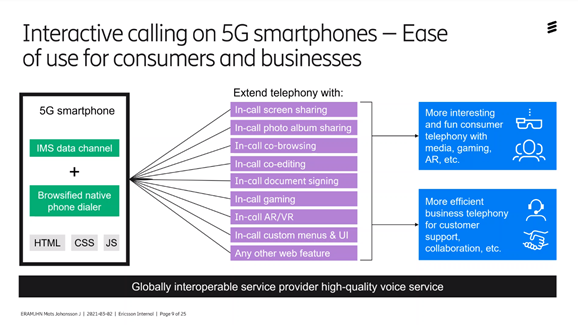
If we look at simply telephony and voice, we get better functions for speech/message etc. built into 5G so that you do not have to download apps to be able to run video meetings, share pictures etc.
If we look into industrial applications, for example in manufacturing, where robots are usually connected with wifi or fixed cables. The advantage of fixed cables is that you have short delays, but if you want to switch, it takes time to do this. Robots must have a lot of software in them due to the delays, and with 5G it is thought that the software can be placed in a local 5G network in the factory, where even the robots can communicate with each other and correct errors, which means that you never have to stop production.
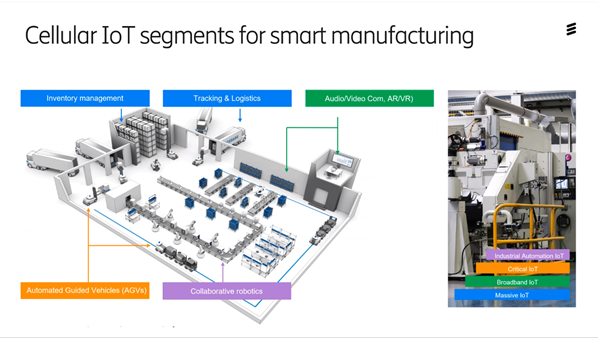
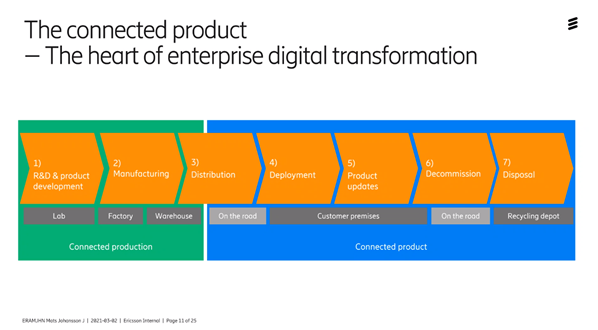
In warehouse management, there are several opportunities with 5G. You can keep track of where all products are with driverless trucks run by 5G network. There is a great deal of interest in the industrial sector for this type of solution. If you look at production, you see that it will be a digitized chain where the product is connected throughout its life cycle right up to completion and recycling.
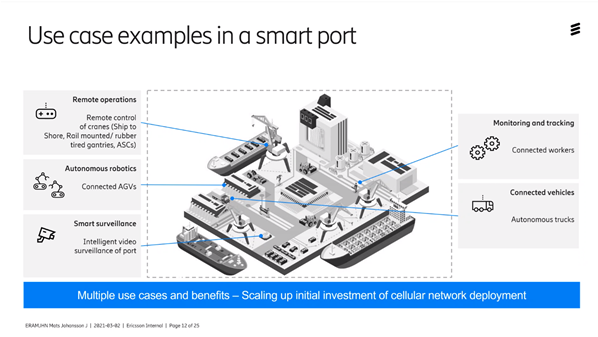
Several projects are already underway today in the development of mobile networks for ports. As 90% of all shipping takes place via ports, unloading, loading can be improved and made more efficient through the new way of connecting products and services.
What value does 5G add?
The value of 5G increases with the complexity of the transactions to be performed. From simpler documentation and data collection to being able to proactively control production and processes but also automate processes on a industrial scale.
If we look at the area of virtualization of consumer products. In 1991, you had to buy each product separately. If you needed a video camera, you bought one and if you needed a regular camera, you had to buy another device. Then came the smartphone revolution when you could buy a product that handled all the functions virtualized, such as those listed in the flyer below.

Technically, what happened was a development of a general hardware with a virtualization layer (iOS or Android) and all applications in an app store and the result was a smartphone. Users then had the opportunity to change apps themselves, upgrade their hardware, install new apps and upgrade the operating system and change hardware without removing all apps.
The same development needs to happen to the telecom network, where you need to make the network as virtualized as you did with the smartphone. The difference here is that the network must always be up and running even during the upgrade, which is a challenge, which is why this transformation will take many years.
What is a 5G network?
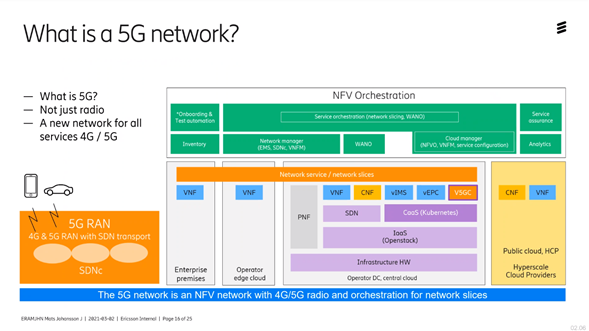
The core network is rebuilt so that it becomes a data center, instead of separate nodes as today, then a virtualization layer is added. All IP networks are managed within the data center (DC) and between DCs become programmable. The physical nodes become software parts so-called. virtual network functions.
Ericsson will build all applications as software and that development has been underway for a few years. Today, 30-40% of all traffic goes in this type of network. The networks that exist today consist of physical networks and still consist of 2G, 4G, etc., so all networks coexist for many years to come. Operators will distribute data centers in more places in a country and also allow companies to have their own network. The benefits will be to be able to move applications to get closer to the end-users and get shorter delays.
There will also be a collaboration with what are called "Public Clouds", such as Amazon, Azure, or Google where applications are developed today. They must be able to use the mobile network, with all its existing customers and applications.
As for the radio side in 5G, you will get improvements such as new frequencies, wider bands to work with, more advanced antenna systems.
It will be possible to direct the radiation to where people are located. You can also make special lobes so that the net follows, for example, moving cars.
Being able to distribute the network becomes important based on where the data center is located to reduce the delay with the distance. You then need to build more data centers and it will develop as time goes on.
Another important improvement with 5G is that you will be able to work with "Network slicing". This means that you create a virtual part of the entire network so that, for example, a railway train has a part that handles the passengers' surfing and the other part handles the train's functions, so that these are separated from each other.
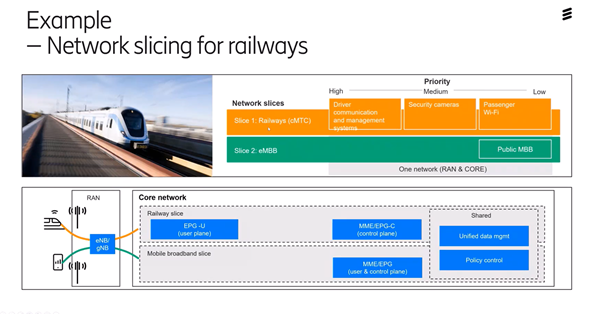
The orange part of the image has a different quality and priority. This will be an important part as you can use the entire 5G network more efficiently for all types of services and give them exactly the resources they need, then you do not risk congestion in the network by consumers.
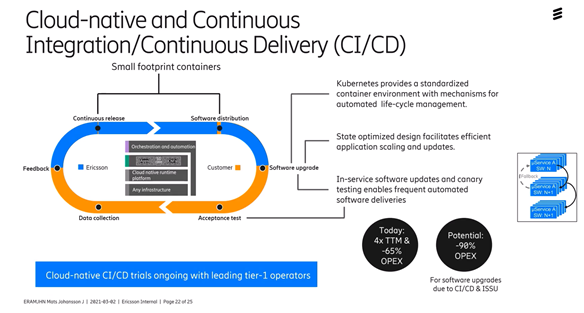
Upgrading an entire network today is advanced and expensive, so what will also be required is to rebuild the network, through "Cloud-native" you will be able to upgrade small pieces often. So instead of large releases, you will be able to perform weekly upgrades more often.
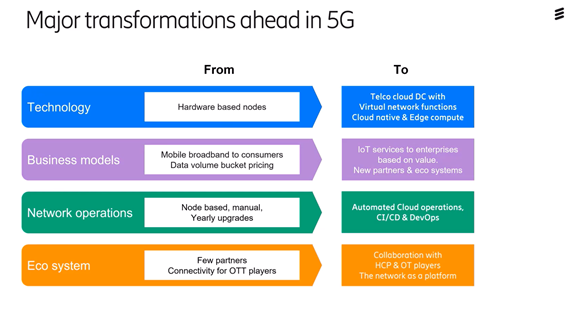
In summary, there are big upcoming changes that will take place in several large areas.
Technically, we go from hardware nodes to "Telco cloud" with virtual functions in. We develop Cloud native and Edge computing.
The business models need to change from just being focused on mobile broadband to consumers into getting IoT services based on value, and getting new partners and app developers to work with it.
There will also be a transformation in how we handle the networks, from today's node-based where much is done manually to tomorrow's which is more automated.
An ecosystem must be built up as there are few partners onboard today. The top players like Google, Netflix and Facebook do not pay the operators anything special to use the network, but take a large part of the value in the value chain. The operators will in the future be able to take a larger part of the value chain by collaborating with the cloud players and larger companies that today integrate the automated solutions in large factories and the like.
5G will be a platform for innovation where anyone can innovate. The complexity in society will increase enormously and therefore automation must be introduced. If you do not, you will not be able to build a data center with all the beneficial functions for all players and an upgraded better digital future will not happen.
What security demands will 5G require?
We will probably not see the flagship case - self-driving cars and remote surgery first, as safety will be a priority. When you open up the networks for IoT, the security risk also increases, so you have worked hard to increase the standardized security in the network, together with well-developed processes for handling secure products. It is very much about monitoring a network in terms of security as well, firewalls are not enough, but you must be able to monitor the networks and build effective action processes.
What time horizon do you see of the development of 5G?
The 5G evolution mentioned above will progress under at least 10 years, maybe longer and in the meantime 6G will come, so the biggest shift will be to go from consumer network to broad industrial network.
Do you have any consulting assignments in 5G development?
Yes, contact A Society and we will lead you to the right person to see how your skills can benefit both the customer and you as a consultant.
You find our contact information under A Society's contact page.
A Society is the consulting company of tomorrow and can help consultants connect with customers who are looking for consultants in 5G development.

